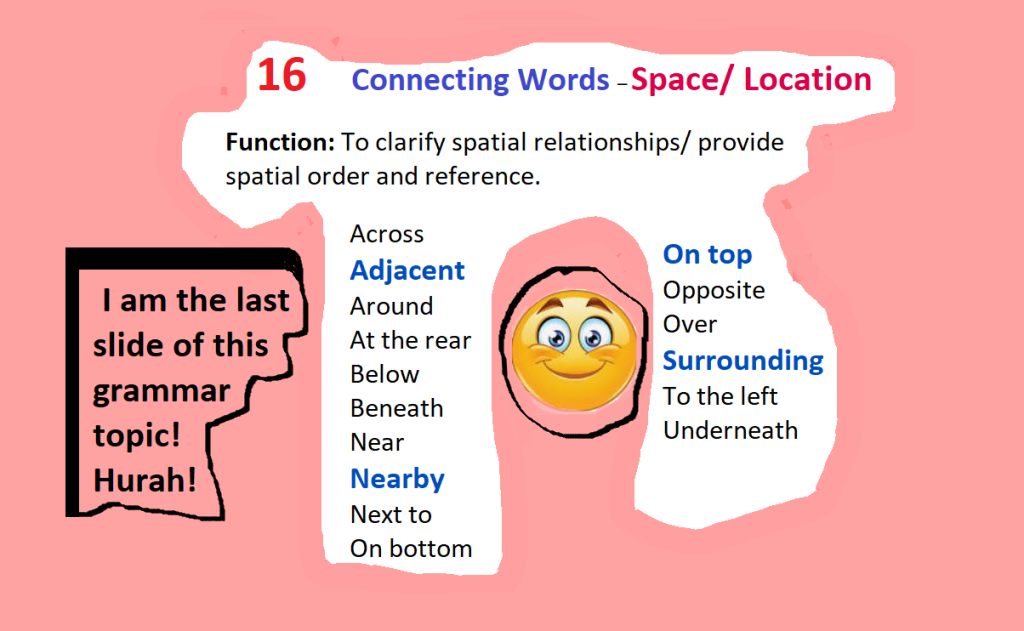
BASIC/EASY TRANSITION WORDS
for
Beginners/High Beginners (ESL)

List of Linking Words
&
Connecting Words
(in 10 color cards)
For Students’ Writing
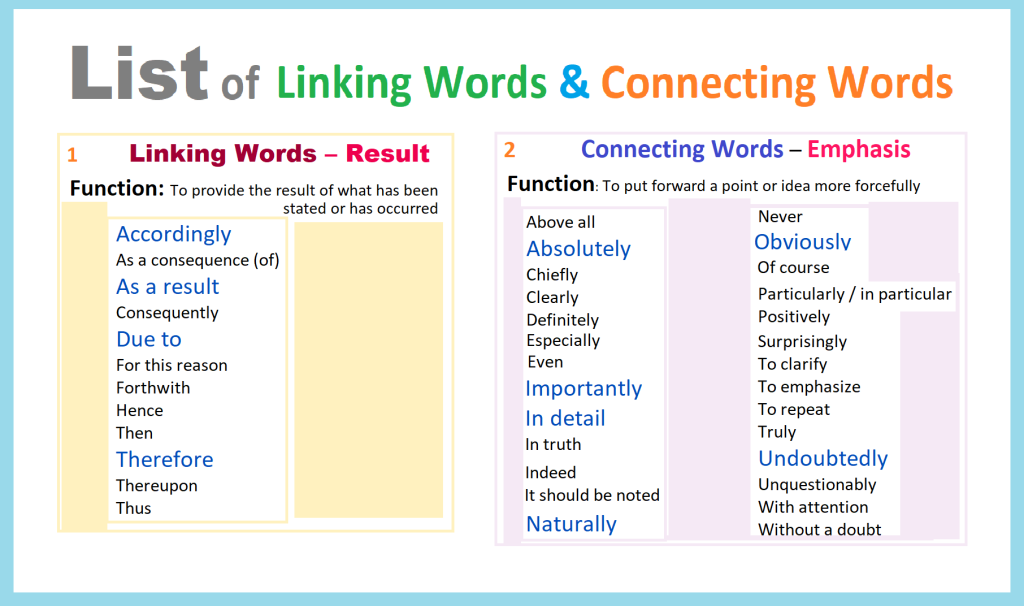

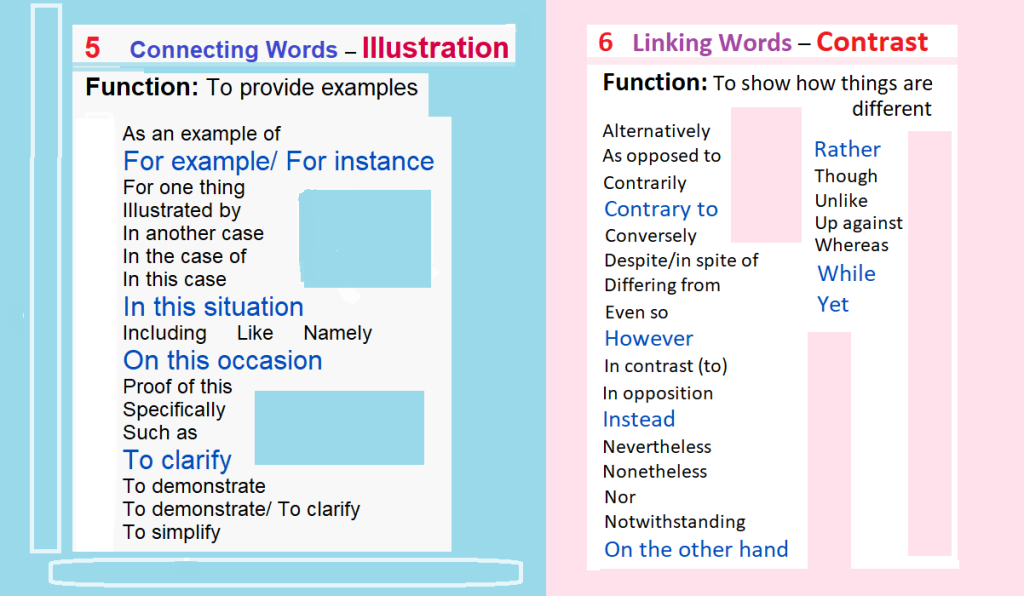




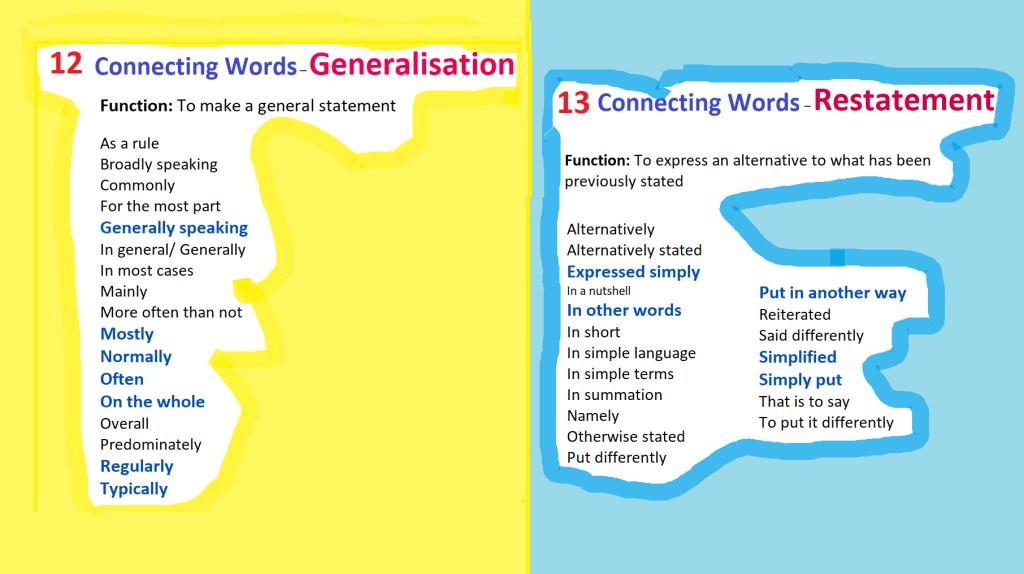
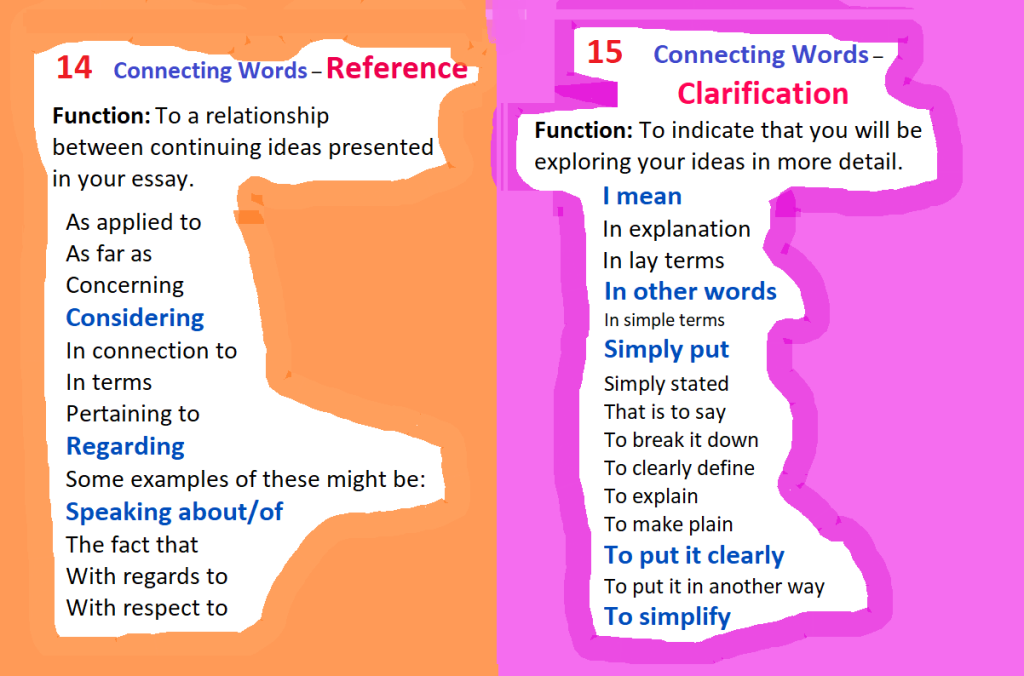
Posted by Zoia Eliseyeva on September 21, 2022 from Arizona, USA: in Preparation for my Reading/Writing Classes in FALL2022

Avoiding Run-On Sentences: Explanation and Practice
Spring 2024
ESL-010.3-31161: High Beg Speak/Listen
M/W 4:30 PM – 7:45 PM
2/13/2024 TUE – 6/5/2024
Hesp, W-24
ESL-010.1-31156: Listening & Speaking Level 1
M/W 8:00 AM – 11:25 AM
2/14/2024 WED – 6/5/2024
Hesp, W-25
Class Weekly Calendar
Week Date / Monday & Wednesday
1 2/12 2/14 Lincoln Mo No Class
2 2/19 2/21 Washington Mo No Class
3 2/26 2/28
4 3/4 3/6
5 3/11 3/13
6 3/18 3/20
7 3/25 3/27
8 4/1 4/3
9 4/8 4/10 (Entire week Spring Break No Classes)
10 4/15 4/17
11 4/22 4/24
12 4/29 5/1
13 5/6 5/8
14 5/13 5/15
15 5/20 5/22
16 5/27 5/29 Memorial MON No Class
17 6/3 6/5
Syllabus Fall 2023 ESL 010-3-73526 High Beg. Hybrid (starts 9/25/2023 Mon)
https://docs.google.com/document/d/196Y4d5HqogZ4h5kfpYXtIDt-ubnZ43K5SbOqL145b7I/edit?usp=sharing
Syllabus Fall 2023 ESL 010-5 – 73264 (91992) ESL Lvl 3 Low Int. (starts 8/15/23 Tue)
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1RlQ6lXtYHpIjM4kwDcZiNtIixd8JbSdfDEMWCSDWzQA/edit?usp=sharing
Syllabus Spring 2023, ESL-010.4-31163: the class starts March 14, 2023: ENGLISH Grammar & Vocabularyhttps://docs.google.com/document/d/1Tkm9x46BlEFQ7Q9C4CQBErgsvVGSlypbtC7lvLw_7Xo/edit?usp=sharing
Copy of ESL 10-6 Jan 31 2023 1st Class App Vall – Google Docs
Syllabus Spring 2022, AENG 10.4 – 82604 (Morning) – Starts on March 15, 2022 (Tuesday) (VVC, Hesperia Campus, CA, USA)
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1_d3fyk5AQYo-syONNHoLwteFwiNrF-HINZ3_r5eDRe0/edit?usp=sharing
Syllabus SPRING 2022, ESL-2, Starts March 14, 2022 (Monday) – Zoom Class
(VVC, California, USA)
https://drive.google.com/file/d/190Z58kNegjjnrmMsZZvvUBqdht60jY14/view?usp=sharing
How to register for Spring 2021 semester ONLINE Beginners’ Class:
Go to the college website:
1) Find the Subject “Adult Education English” (AENG)
2) Choose the semester “Spring 2021”
3) Find the class by name of instructor “Zoia Eliseyeva”
AENG-10.1-78159 Low Beg Speak/Listen
Spring 2021 Term Instructors Eliseyeva, Z
Meeting Information M, W 7:45 AM – 11:05 AM
2/17/2021 – 6/9/2021 (Hesperia High School), Zoom CANVAS (Laboratory/Studio/Activity)
Dates 2/16/2021 – 6/12/2021
To register: vvc. edu 1) Find the Subject “Adult Education English” (AENG) 2) Choose the semester “Spring 2021” 3) Find the class by name of instructor “Zoia Eliseyeva”
Verbs Followed by Gerunds or Infinitives
Verbs Followed by the Gerund
acknowledge
admit
advise
appreciate
avoid
can’t help
can’t stand
celebrate
consider
delay
deny
detest
discontinue
discuss
dislike
endure
end up
enjoy
escape
explain
feel like
finish
forgive
give up (stop)
imagine
justify
keep (continue)
mention
mind (object to)
miss
postpone
practice
prevent
prohibit
put off
quit
recall
recommend
regret
report
resent
resist
risk
suggest
support
tolerate
understand
Verbs Followed by the Infinitive
agree
appear
arrange
ask
attempt
can’t afford
can’t wait
choose
consent
decide
deserve
expect
fail
help
hesitate
hope
hurry
intend
learn
manage
mean (intend)
need
neglect
offer pay plan
prepare
pretend
promise
refuse
request
rush
seem
volunteer
wait
want
wish
would like
Verbs Followed by the Gerund or the Infinitive
begin
can’t stand
continue
forget*
hate
like
love
prefer
remember*
start
stop*
try
* a big difference in meaning if used Ger or Inf
Verbs Followed by Object+ Infinitive
advise
allow
ask*
cause
choose*
convince
encourage
expect*
forbid
force
get
help*
hire
invite
need*
pay*
permit
persuade
promise*
remind
request
require
teach
tell
urge
want*
warn
wish
would like*
*these verbs can also be followed by an infinitive without an object (example: ask to leave or ask someone to leave).
Examples:
1. I enjoy singing (“enjoy” takes only GERUND)
2. I like to read. Or I like reading. (“like” takes
both: either INFINITIVE or GERUND)
3. I want to study French. (“want” takes only
INFINITIVE)
4. Help him do it. (“help” is followed by Object plus
INFINITIVE)
++++++++End of English Grammar Point posted Jan 11 2019++++++++
Past Simple, Past Perfect, and Would as a Modal
Example-paragraph from British literature
(John Fowles)
Then it was strange, she smiled just like she was going to laugh, and then she stopped and turned and went into her room, where I followed with the tray.
She poured out the tea, but something had made her angry, you could see.
She wouldn’t look at me.
Past Simple
was
smiled
was going to (intention)
stopped
turned
went
followed
poured out
could (Past tense of the modal “can”)
Past Perfect
had made (the timing is before all the actions expressed with Past Simple)
Would as a Modal
(as compared with its usage as “Future-in-the-Past” – in this case it is a different usage)
wouldn’t (she did not want to, she was not willing to, she was doing that intentionally)
+++End of Grammar Point about Past tenses in literature on June 30, 2020+++
Commas (Eight Basic Uses) https://docs.google.com/document/d/1owH9v9TZonFHFNSJPML4s_i40PGEGiLiSLYpakzzwksThe Prince and the Pauper English Russian Video of Chapter 24 Mark Twain: Literature
English Grammar Point: Subjunctive after Verbs of Request
SUBJUNCTIVE VERBS OF REQUEST ENGLISH GRAMMAR
English Grammar Point: Subjunctive after Expressions of Urgency
SUBJUNCTIVE EXPRESSIONS OF URGENCY ENGLISH ESL GRAMMARsions of Urgency ENGLISH LESSON My Movie
Table of English Irregular Verbs
Syllabus SPRING 2020 VVC Hesperia Instructor: Zoia Eliseyeva
A Table of Irregular Verbs that you can print out or download:
http://zoiaeliseyeva.com/docs/103_fall_2018/103fall2018_IrregularVerbsTable.pdf
Two Irregular Verbs, that You May Confuse, in Examples (downloadable)
LAY AND LIE :
http://zoiaeliseyeva.com/docs/103_fall_2018/103fall2018_LAY_LIE_TWO_IRREGULAR_VERBS.pdf
If-Sentences
1) We use simple conditional verbs to describe what might be. We use the conditional form other would + verb. Examples: If I go, would you follow? / If you follow, will you bring my coat to me? / If you go, I will you sit with me?
2) We use the future conditional for uncertainites. We use the subjunctive form of “go”, using “went” in the “if” clause: If I went, would you follow? (I really want to go, but I don’t want to go alone.) If I went, would you bring my coat to me? (I really want to go, but I can only be comfortable with my coat.) If I went, would you sit with me? (I really want to go, but I don’t want to be there alone.)
3) We use stronger subjunctive construction for stronger uncertainties. We use the subjunctive form of “go”, using “were to go” in the “if” clause and the subjunctive form of “will”, using “would” in the main clause: If I were to go, would you follow? (I’m thinking that I might go if you followed. Or not.) If I were to go, would you bring my coat to me? (I’mean thinking that I might go if you brought my coat. Or not. ) If I were to go, would you sit next to me? (I’m thinking that I might go if you sat with me. Or not.)
4) We are now talking after-the-fact-subjunctive. These often sound like regrets, so they can sound a little sad: If I had gone, would you have followed? (Maybe we could have some one more memory.) If I had gone, would you have brought my coat to me? (I could already have my coat back.) If I had gone, would you have sat next to me? (I could have had some companionship that night.) This is the language of could’ve/should’ve.



